Introduction
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems have become essential tools for businesses looking to streamline their operations and improve overall efficiency. These integrated software platforms enable organizations to manage various core business functions, including finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management. In this article, we will explore the importance of ERP system implementation and guide you through the essential steps and considerations involved in the process.
Understanding ERP systems
ERP systems are comprehensive software solutions designed to facilitate the flow of information between different departments and functions within an organization. These systems provide a centralized database and a unified interface, allowing users to access and share data in real-time. By integrating various business processes and functions, ERP systems offer a holistic view of an organization’s operations, helping decision-makers make informed choices and drive business growth.
Importance of ERP system implementation
Implementing an ERP system can bring numerous benefits to an organization. Firstly, it allows for better coordination and collaboration between departments, eliminating data silos and ensuring a seamless flow of information. This increased transparency not only improves operational efficiency but also enables faster decision-making and problem-solving.
Moreover, ERP systems provide organizations with the ability to automate routine tasks and repetitive processes, reducing human errors and freeing up valuable resources. This automation can improve productivity and enable employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities, ultimately driving business growth.
Furthermore, by consolidating data from different functional areas into a single system, ERP systems provide businesses with accurate and up-to-date information for effective reporting, analysis, and forecasting. This data-driven approach allows for better strategic planning and helps organizations stay ahead of their competition.
Overall, implementing an ERP system is a strategic investment that can transform the way an organization operates by increasing efficiency, streamlining processes, reducing costs, and improving decision-making capabilities.
Pre-implementation considerations
Before embarking on an ERP system implementation, there are several key considerations that organizations need to address to ensure a successful project.
Assessing organization’s needs and requirements
The first step in the pre-implementation phase is to assess the organization’s needs and requirements. This involves understanding the current processes and workflows, identifying pain points and inefficiencies, and determining the key objectives and desired outcomes for implementing an ERP system. Organizations should involve key stakeholders and department heads in this process to gather comprehensive insights and ensure alignment with business goals.
Identifying key stakeholders
Identifying key stakeholders is crucial for the success of an ERP implementation project. Stakeholders can include top management, department heads, end-users, IT personnel, and external consultants. By involving all relevant stakeholders from the early stages of the project, organizations can gain buy-in, ensure a shared vision, and overcome potential roadblocks more effectively.
Defining project goals and objectives
Defining clear and measurable goals and objectives is essential for ERP implementation success. These objectives may include improving operational efficiency, enhancing data accuracy, reducing costs, or increasing customer satisfaction. Setting realistic and well-defined goals allows organizations to track progress, evaluate the effectiveness of the implementation, and ensure alignment with the overall business strategy.
Planning phase
The planning phase is critical as it lays the foundation for a successful ERP system implementation. It involves the development of a comprehensive project plan, allocation of resources and budget, and establishing a realistic timeline.
Creating a project plan
Creating a project plan involves breaking down the implementation process into smaller, manageable tasks and assigning responsibilities to team members. The project plan should outline key milestones, deliverables, dependencies, and deadlines. It should also include a clear communication and reporting structure to ensure effective collaboration and coordination throughout the project.
Allocating resources and budget
Allocating the right resources is crucial for the smooth execution of an ERP implementation project. This includes assigning a dedicated project team, consisting of both internal employees with relevant expertise and external consultants if necessary. Additionally, organizations should allocate a sufficient budget to cover implementation costs, including software licensing, hardware infrastructure, training, and support.
Establishing a timeline
Establishing a realistic and achievable timeline is a key aspect of successful ERP implementation planning. Organizations should consider factors such as the complexity of their operations, the size of the organization, and the availability of resources. By setting clear deadlines and milestones, organizations can ensure that the implementation process stays on track and avoid unnecessary delays.
System selection
Selecting the right ERP system is a crucial decision that requires careful evaluation and consideration. It involves assessing multiple vendors and solutions, conducting a feasibility study, and making an informed decision based on specific organizational needs.
Evaluating ERP vendors and solutions
When evaluating ERP vendors and solutions, organizations should consider factors such as the vendor’s reputation, industry experience, customer reviews, and the scalability and flexibility of the system. It is essential to assess whether the system can address specific business requirements, integrate with existing software and hardware infrastructure, and provide the necessary functionalities for future growth.
Conducting a feasibility study
Conducting a feasibility study involves assessing the technical, financial, and operational feasibility of implementing an ERP system. This study helps organizations identify any potential risks or challenges associated with the implementation and determine whether the benefits outweigh the costs and efforts involved.
Making an informed decision
Based on the evaluation and feasibility study, organizations can make an informed decision about the most suitable ERP system and vendor for their needs. It is crucial to involve key stakeholders in this decision-making process to ensure alignment with business goals and gain their support for the implementation.
Customization and configuration
Once the ERP system is selected, customization and configuration are essential steps to align the system with specific organizational needs and processes.
Mapping business processes to ERP system
Before customization and configuration, organizations should map their existing business processes and workflows to the ERP system. This involves understanding how the system can support specific operations and identifying areas that require customization or reengineering to optimize efficiency and productivity.
Customizing the system
Customizing the system involves tailoring the ERP software to meet the specific requirements of the organization. This can include configuring user interfaces, defining data fields, creating workflows, and integrating with other software systems. It is important to strike a balance between customization and leveraging standard system functionalities to ensure future upgrades and compatibility.
Configuring modules and functionalities
Configuring modules and functionalities involves setting up various modules within the ERP system, such as finance, human resources, inventory management, and sales. Organizations should configure these modules based on their specific requirements, ensuring that data flows smoothly across different processes within the system.
Data migration
Data migration is a critical step in ERP system implementation, as it involves transferring data from legacy systems to the new ERP platform while ensuring data integrity and accuracy.
Assessing data compatibility and quality
Before migrating data, organizations should assess the compatibility and quality of their existing data. This involves identifying any inconsistencies, redundancies, or data gaps that need to be addressed before the migration process.
Extracting and transforming data
The next step is to extract data from the legacy systems and transform it into a format compatible with the new ERP system. This may require data cleansing, standardization, and validation to ensure data integrity and accuracy.
Loading data into the new ERP system
Once the data is transformed, it can be loaded into the new ERP system. Organizations should ensure that all relevant data is migrated, including master data, transactional data, and historical data. It is important to conduct thorough testing and validation to ensure that data has been successfully transferred and is accurately reflected in the new system.
Testing and validation
Testing and validation are essential steps in the ERP implementation process to ensure the system’s performance, functionality, and reliability.
Conducting system testing
System testing involves testing the various modules and functionalities of the ERP system to verify their accuracy and reliability. This includes performing unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing to identify any issues or errors that need to be addressed.
Evaluating system performance and functionality
Organizations should evaluate the system’s performance and functionality to ensure that it meets the predefined goals and objectives. This includes reviewing key performance indicators, analyzing system response times, and evaluating user experience. Any identified issues or gaps should be addressed before proceeding to the next phase.
Addressing any issues or errors
If any issues or errors are identified during testing and validation, they should be promptly addressed and resolved. This may involve working closely with the ERP vendor or engaging external consultants to provide support and guidance.
Training and user adoption
Training and user adoption are crucial for the successful implementation and utilization of an ERP system within an organization.
Developing a training plan
Developing a comprehensive training plan is essential to ensure that all users can effectively utilize the new ERP system. The training plan should include both initial training sessions and ongoing support to address any questions or challenges that arise during the transition.
Conducting user training sessions
User training sessions should be conducted to familiarize employees with the new ERP system’s functionalities, workflows, and processes. These sessions should be tailored to different user roles and responsibilities within the organization and provide hands-on training to ensure practical knowledge transfer.
Promoting user adoption and acceptance
Promoting user adoption and acceptance is crucial for the success of an ERP implementation. Organizations should emphasize the benefits of the new system, provide ongoing support and guidance, and address any resistance or concerns from users. It is important to create a positive and inclusive environment that encourages employees to embrace and utilize the new system effectively.
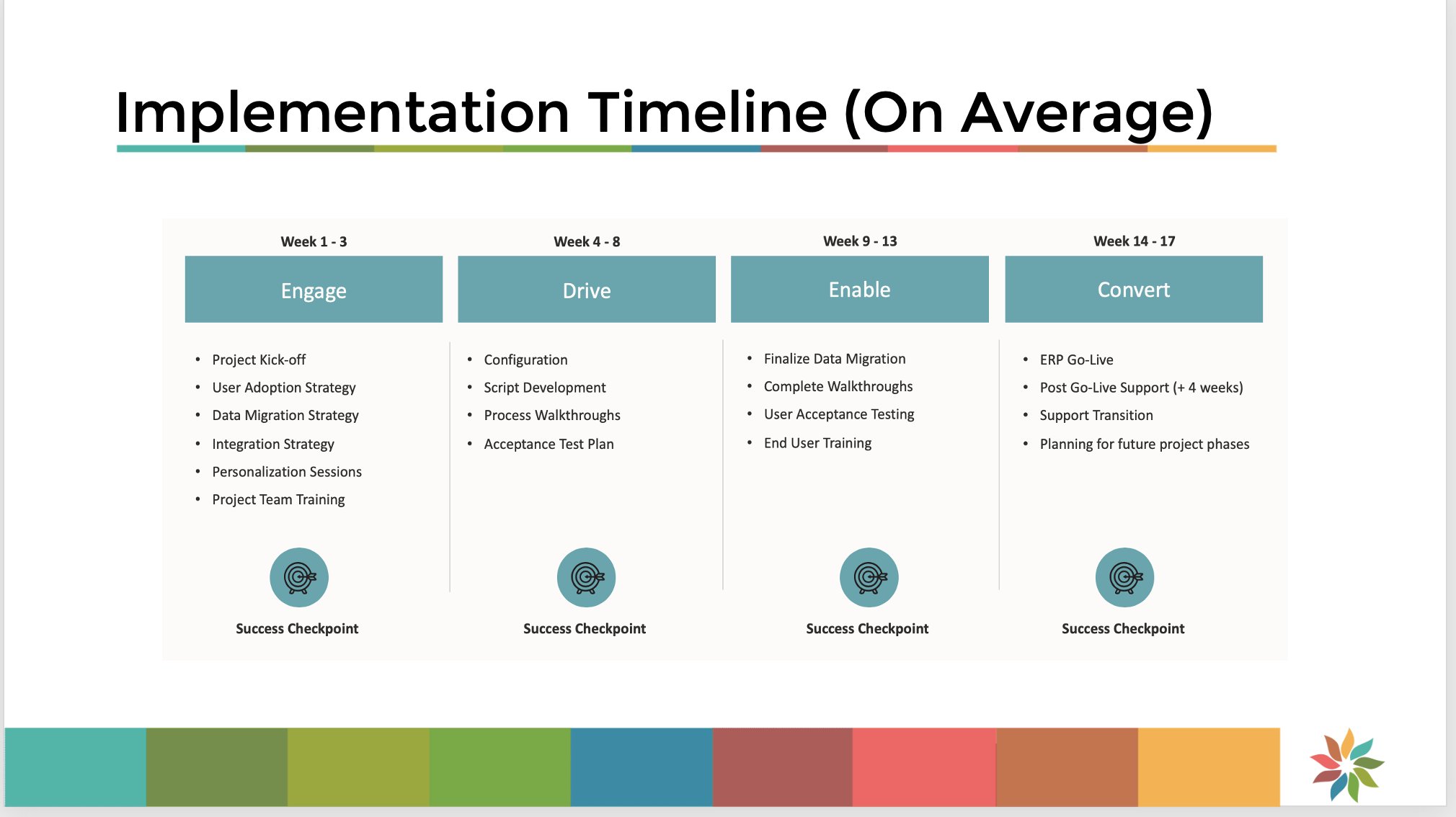
Go-live and post-implementation support
The go-live phase marks the official launch of the ERP system within the organization. It is followed by post-implementation support and maintenance to ensure the system’s stability and continuous improvement.
Executing the final implementation steps
During the go-live phase, organizations should execute the final implementation steps, including data migration, system configuration, and user access setup. It is crucial to ensure that all stakeholders are informed about the go-live date and any changes or disruptions that may occur during the transition.
Monitoring system performance and stability
After the go-live, organizations should closely monitor the system’s performance and stability to identify any potential issues or bottlenecks. This monitoring can include regular system health checks, data audits, and user feedback. Proactive measures should be taken to address any emerging issues and optimize system performance.
Providing ongoing support and maintenance
Ongoing support and maintenance are essential to ensure the long-term success of an ERP system. This includes providing technical assistance, addressing user inquiries and issues, and performing regular system updates and upgrades. Organizations should establish a support mechanism and a dedicated team to manage post-implementation activities effectively.
Factors influencing implementation time
Several factors can influence the duration of an ERP system implementation. Understanding these factors is crucial for setting realistic expectations and planning accordingly.
Organization size and complexity
The size and complexity of an organization can significantly impact the implementation time. Larger organizations with multiple departments and complex workflows may require more extensive customization and configuration, leading to a longer implementation timeline.
Degree of customization required
The degree of customization required can also influence the implementation time. Organizations that have unique requirements and complex business processes may need more time to configure the system and integrate it with existing infrastructure.
Availability of resources and expertise
The availability of resources and expertise within the organization can impact the implementation time. If the organization lacks the necessary resources or expertise to manage the implementation internally, it may need to engage external consultants or rely on the ERP vendor for support, which can prolong the timeline.
Common challenges and potential delays
Implementing an ERP system comes with its own set of challenges, which can lead to potential delays if not properly addressed.
Resistance to change
Resistance to change is a common challenge in ERP implementation projects. Employees may be hesitant to adopt new processes and technologies, fearing job displacement or increased workload. Organizations should invest in change management strategies, including effective communication, training, and ongoing support, to overcome this resistance and ensure successful adoption.
Inaccurate initial project planning
Inaccurate initial project planning can lead to delays and cost overruns. Organizations must invest sufficient time and effort in the planning phase to gather accurate requirements, evaluate risks, and set realistic timelines and budgets. Regular monitoring and evaluation throughout the implementation process can help identify and address any discrepancies or deviations from the initial plan.
Integration issues with existing systems
Integration issues with existing systems can cause delays and disruptions during the ERP implementation. Organizations should conduct a thorough assessment of their current IT landscape, perform compatibility tests, and develop a robust integration strategy to ensure smooth data flow and interoperability between the ERP system and other systems.
Success factors for timely ERP implementation
While ERP implementations can be complex and time-consuming, several success factors can help ensure timely delivery and a smooth transition.
Strong project management and leadership
Strong project management and leadership play a crucial role in ERP implementation success. Clear communication, effective delegation, and proactive risk management are essential to keep the project on track and address any challenges that may arise.
Effective communication and collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are critical throughout the implementation process. Regular updates, transparent reporting, and open lines of communication between stakeholders, project team members, and end-users help maintain alignment, manage expectations, and address any issues or concerns promptly.
Regular monitoring and evaluation
Regular monitoring and evaluation allow organizations to track progress, identify potential bottlenecks, and take corrective actions as needed. This includes assessing key performance indicators, conducting user surveys, and soliciting feedback from the project team and end-users. Continuous improvement and learning from past experiences help optimize the implementation process.
Realistic timeline estimation
Estimating a realistic timeline for ERP system implementation is crucial to manage expectations and ensure project success.
Industry standards and benchmarks
Organizations can gain insights into realistic timeline estimates by referring to industry standards and benchmarks. Understanding the average implementation duration for similar organizations in the same industry can provide a baseline for planning and resource allocation.
Consulting with ERP implementation experts
Engaging ERP implementation experts and consultants can help organizations assess their specific needs and develop a realistic timeline. These experts bring specialized knowledge and experience from previous implementation projects, enabling organizations to make more accurate estimations.
Accounting for potential delays
When estimating the timeline, organizations should account for potential delays due to unforeseen circumstances, such as technology issues, data quality challenges, or changes in business requirements. Building in buffer time and contingency plans can help mitigate risks and ensure a smoother implementation process.
Case studies and examples
Examining real-life case studies and examples can provide valuable insights into ERP system implementation durations.
Short implementation durations
Some organizations have been able to successfully implement an ERP system within a relatively short timeframe. For example, Company XYZ, a mid-sized retail company, completed its ERP implementation in eight months by following a streamlined project plan, engaging a dedicated project team, and leveraging the expertise of an ERP implementation partner.
Lengthy implementation durations
On the other hand, large organizations with complex operations may experience longer implementation durations. For instance, Company ABC, a multinational manufacturing company, took two years to complete its ERP implementation due to its extensive customization requirements, global rollout, and the need to integrate with multiple legacy systems.
Conclusion
Implementing an ERP system is a complex and critical undertaking for any organization. By carefully considering pre-implementation factors, planning diligently, selecting the right system, customizing and configuring effectively, migrating data meticulously, conducting thorough testing, providing comprehensive training, and backing it up with post-implementation support, organizations can ensure a successful and timely ERP implementation. The process requires strong project management, effective communication, and collaboration, as well as a realistic estimation of the timeline. Despite the potential challenges, the benefits of a successful ERP implementation, including increased efficiency, streamlined processes, and data-driven decision-making, make the effort well worth it.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an ERP system?
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is a software solution that integrates and manages various core business functions, such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management. It provides a centralized database and a unified interface, enabling real-time access and sharing of information within an organization.
2. How long does an ERP implementation typically take?
The duration of an ERP implementation can vary depending on factors such as the organization’s size, complexity, degree of customization, and availability of resources. On average, ERP implementations can take anywhere from several months to a few years.
3. What are some common challenges in ERP system implementation?
Some common challenges in ERP system implementation include resistance to change, inaccurate initial project planning, and integration issues with existing systems. These challenges can lead to potential delays if not properly addressed through change management strategies, comprehensive planning, and robust integration frameworks.
4. How important is user training and adoption in ERP implementation?
User training and adoption are crucial for the successful implementation and utilization of an ERP system. Organizations should invest in developing a comprehensive training plan, conducting user training sessions, and promoting user adoption through ongoing support and communication. This ensures that employees can effectively utilize the system and maximize its benefits.
5. How can organizations estimate a realistic timeline for ERP implementation?
Organizations can estimate a realistic timeline for ERP implementation by referring to industry standards and benchmarks, consulting with ERP implementation experts, and accounting for potential delays. It is important to factor in the organization’s size, complexity, and available resources when estimating the timeline. Building in buffer time and contingency plans can help manage risks and ensure a smoother implementation process.